Surface normal estimation of thin transparent objects from polarization of transmitted light
Surface normal estimation of thin transparent objects from polarization of transmitted light |
|
 |
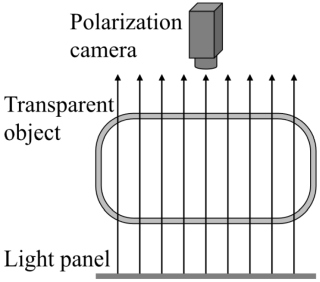
In this paper, we propose a novel method for estimating the surface shapes of transparent objects by analyzing the polarization state of the transmitted light. The target objects are thin transparent objects, such as bottles or glasses. Thin transparent objects less refract, thus, existing methods that analyze the light transport for shape estimation fail. On the other hand, our polarization-based method can estimate the unique surface normal of thin transparent object. |
| [1] Akihito Watanabe, Daisuke Miyazaki, "Surface normal estimation of thin transparent objects from polarization of transmitted light," 2022.8 | |
Image enhancement for dichromats using image pyramid based on saturation |
|
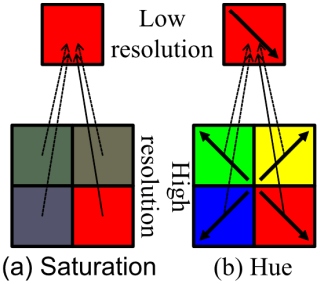 |
To extend the ability of dichromats to recognize the color difference, we propose a method to expand the color difference when observed by dichromats. We analyze the color between the neighboring pixels in chromaticity space. In addition, we employ multiresolution analysis to form the Poisson equation. Our multiresolution analysis is non-linear depending on the saturation of each pixel's color. Solving the multiresolution Poisson equation results in the color enhanced image. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Hodaka Tanida, "Image enhancement for dichromats using image pyramid based on saturation," 2022.8 | |
Specular removal of monochrome image using polarization and deep learning |
|
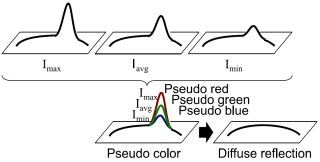 |
We have proposed a method to remove specular reflection from a single polarization image. Most existing methods use color information for specular removal, however, those methods can neither be applied to monochrome images nor achromatic objects. To overcome this problem, we use polarization for specular removal. Most methods not only use polarization camera but also use polarized light, while we use polarization camera and unpolarized light. In addition to polarization, we also use a deep neural network to stably remove specular reflection in a grayscale image. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Naoto Yoshimoto, "Specular removal of monochrome image using polarization and deep learning," 2022.6 | |
Example-based multispectral photometric stereo for multi-colored surfaces |
|
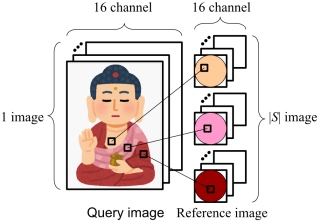 |
This paper use example-based photometric stereo for solving the problem of color photometric stereo. Color photometric stereos suffer from mathematical difficulty, and they add many assumptions and constraints, however, example-based photometric stereo is free from such mathematical problems. The process of our method is pixelwise, thus, the estimated surface normal is not oversmoothed, unlike existing methods that use smoothness constraints. To demonstrate the effectiveness of this study, a measurement device that can realize the multispectral photometric stereo method with 16 colors is employed instead of the classic color photometric stereo method with 3 colors. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Kazuya Uegomori, "Example-based multispectral photometric stereo for multi-colored surfaces," Journal of Imaging, vol. 8, no. 4, article no. 107, 13 pages, 2022.4 | |
Color exaggeration for dichromats using weighted edge |
|
 |
To extend the ability of dichromats to recognize the color difference, we propose a method to expand the color difference when observed by dichromats. We analyze the color between the neighboring pixels not in intensity space but chromaticity space and form a Poisson equation. In addition, we use the sigmoid function to weigh the edge of a color image. The color difference can be adequately tuned manually by the weight parameter so that the dichromats can obtain the image that they want where the visibility of the color is enhanced. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Harumichi Morimoto, "Color exaggeration for dichromats using weighted edge," The International Workshop on Frontiers of Computer Vision, pp. 18-33, 2022.2 | |
Multi-band Photometric Stereo Using Random Sampling of Channels and Pixels |
|
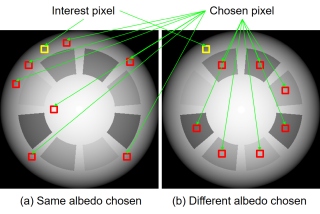 |
This paper estimates the surface normal of a multi-colored object under multi-spectral lighting. This is a difficult problem since the albedo is different for each pixel and each channel. We solve this problem by sampling some pixels randomly. If we randomly sample neighboring pixels, the probability of picking the same albedo pixels may be high. Therefore, if the sampled pixels all have the same albedo, we can determine the surface normal uniquely. To demonstrate the effectiveness of this study, a measurement device with seven colors is used. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Koumei Hamaen, "Multi-band photometric stereo using random sampling of channels and pixels," The International Workshop on Frontiers of Computer Vision, pp. 64-79, 2022.2 | |
Hue Enhancement for Dichromats Using Poisson Equation |
|
   |
In order to extend the ability of dichromats to recognize the color difference, the authors propose a method to expand the color difference when observed by dichromats. Most methods analyze the color in color space, while their method analyze the color in image space. Namely, they analyze the color between the neighboring pixels not in intensity space but in chromaticity space, and form a Poisson equation. Solving the Poission equation results in an image for dichromats whose relative color difference between neighboring pixels is as same as the image observed by trichromats. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Shingo Fujimura, "Hue enhancement for dichromats using Poisson equation," Journal of Imaging Science and Technology, vol. 66, no. 1, article no. 010502, pp. 1-8, 2022.1 | |
Shape from Shading and Polarization Constrained by Approximate Shape |
|
  |
We propose a method which estimates the surface normal from shading information and polarization information. Unlike photometric stereo techniques which use three lights, shape-from-shading uses a single light and is an ill-posed problem. Therefore, to uniquely determine the surface normal using a shape-from-shading method, additional assumptions or additional inputs are required. We use polarization for additional input, because polarization can constrain the surface normal. One example of common assumption is to limits the target object to be a single color, but such assumption restricts the application field. Therefore, we use an approximate shape of the object to solve this problem. Thanks to this approximate shape, we can estimate the surface normal of multi-colored object. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Wataru Muraoroshi, "Shape from shading and polarization constrained by approximate shape," International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), P2-12, pp. 1-5, 2021.7 | |
Surface Normal Estimation from Polarization and Shading under The Convexity Assumption |
|
  |
In this paper, polarization is applied to shape estimation. Surface normal estimation from a single image is commonly performed by shape-from-shading. An alternative approach is shape-from-polarization, which usually cannot uniquely determine the surface normal and must be accompanied by additional information. To resolve this problem, we assume that the object surface is locally convex. Under this assumption, we show that the surface normal can be uniquely determined from the gradients of the shading information. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Naoki Kodama, "Surface normal estimation from polarization and shading under the convexity assumption," Optical Review, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 411-424, 2021.7 | |
Uncalibrated Photometric Stereo Refined by Polarization Angle |
|
  |
In uncalibrated photometric stereo, the light source direction is unknown; thus, both the light source direction and surface normal should be estimated, which establishes an ill-posed problem with ambiguity in its solution. To improve surface normal estimation, we analyze the polarization state of reflected light considering that polarization can constrain the possible orientation of the surface normal. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Shuhei Hashimoto, "Uncalibratred photometric stereo refined by polarization angle," Optical Review, vol. 28, no. 1, pp. 119-133, 2021.1 | |
Multispectral Photometric Stereo Using Intrinsic Image Decomposition |
|
  |
Intrinsic image decomposition can produce the intrinsic image which is not affected by the reflectance. Since the intrinsic image is the image with white object, we can obtain the surface normal by applying the conventional photometric stereo algorithm to the intrinsic image. To demonstrate the effectiveness of this study, a measurement device that can realize the multispectral photometric stereo method with seven colors is employed instead of the classic color photometric stereo method with three colors. |
| [1] Koumei Hamaen, Daisuke Miyazaki, Shinsaku Hiura, "Multispectral Photometric Stereo Using Intrinsic Image Decomposition," International Workshop on Frontiers of Computer Vision, OS5-1, 16 pages, 2020.2 ***Best Paper Award*** | |
Shape Estimation of Concave Specular Object from Multiview Polarization |
|
 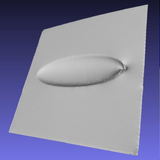 |
This paper proposes a method to estimate the surface normal of concave objects. The target object of our method has specular surface without diffuse reflection. We solve the problem by analyzing the polarization state of the reflected light. However, polarization data from a single view has an ambiguity, and cannot uniquely determine the surface normal. In order to solve this problem, the target object should be observed from two or more views. However, the polarization of the light should be analyzed at the same surface point through different views. In order to get out of a tough spot, we assume that the target object is almost planar. Under this assumption, the surface normal of the object is uniquely determined. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Ryosuke Furuhashi, Shinsaku Hiura, "Shape estimation of concave specular object from multiview polarization," Journal of Electronic Imaging, vol. 29, no. 4, 041006, 23 pages, 2020.1 | |
Extending The Visibility of Dichromats Using Histogram Equalization of Hue Value Defined for Dichromats |
|
   |
In order to extend the ability of dichromats to recognize the color difference, we proposed a method to expand the color difference when observed by dichromats. We have defined a hue variable for dichromats and implemented to our algorithm. We applied the histogram equalization to the hue of dichromats in order to enlarge the color difference recognized by dichromats. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Sayaka Taomoto, Shinsaku Hiura, "Extending the visibility of dichromats using histogram equalization of hue value defined for dichromats," International Journal of Image and Graphics, vol. 19, no. 3, 1950016, 13 pages, 2019.7 | |
Color Photometric Stereo Using Multi-Band Camera Constrained by Median Filter and Occluding Boundary |
|
 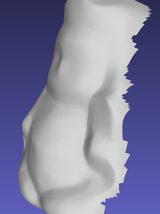 |
In this study, a median filter is employed as the constraint condition of albedo, and the surface normal of occluding boundary is employed as the constraint condition of surface normal. By employing a median filter as the constraint condition, the smooth distribution of the albedo and normal is calculated while the sharp features at the boundary of different albedos and normals are preserved. The surface normal at occluding boundary is propagated into the inner part of object region, and forms the abstract shape of the object. Such surface normal gives a great clue to be used as an initial guess to the surface normal. To demonstrate the effectiveness of this study, a measurement device that can realize the multispectral photometric stereo method with seven colors is employed instead of the classic color photometric stereo method with three colors. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Yuka Onishi, Shinsaku Hiura, "Color Photometric Stereo using Multi-band Camera constrained by Median Filter and Occluding Boundary," Journal of Imaging, vol. 5, no. 7, 64, 29 pages, 2019.7 | |
Uncalibrated Photometric Stereo Constrained by Intrinsic Reflectance Image and Shape from Silhouette |
|
 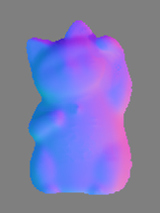 |
Uncalibrated photometric stereo which estimates both light source direction and surface normal is an ill-posed problem, and has ambiguity for solving the problem. Our method employs the idea of intrinsic image decomposition, and estimates the reflectance solely from input image sequence. In addition, we estimate the approximate shape from images without using other sensors such as laser range sensor. This paper reveals that the uncalibrated photometric stereo can be solved by these two constraints. |
| [1] Shuhei Hashimoto, Daisuke Miyazaki, Shinsaku Hiura, "Uncalibrated photometric stereo constrained by intrinsic reflectance image and shape from silhouette," International Conference on Machine Vision Applications, 01-05, pp. 1-6, 2019.5 | |
Surface Normal Estimation of Black Specular Objects from Multiview Polarization Images |
|
  |
The proposed method estimates the surface normal of black specular objects through polarization analysis of reflected light. A unique surface normal cannot be determined from a polarization image observed from a single viewpoint; thus, we observe the object from multiple viewpoints. To analyze the polarization state of the reflected light at the corresponding points when observed from multiple viewpoints, the abstract shape is predetermined using a space carving technique. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Takuya Shigetomi, Masashi Baba, Ryo Furukawa, Shinsaku Hiura, Naoki Asada, "Surface normal estimation of black specular objects from multiview polarization images," SPIE Optical Engineering, vol. 56, no. 4, pp. 041303-1-041303-17, 2016.09 | |
Optimization of LED Illumination for Generating Metamerism |
|
 |
In this article, the authors propose a method for creating trick artwork using metamerism. Two illuminants are designed to achieve metamerism such that two oil paints used in a piece of artwork look the same under one light but different under another light. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Mia Nakamura, Masashi Baba, Ryo Furukawa, Shinsaku Hiura, "Optimization of LED illumination for generating metamerism," Journal of Imaging Science and Technology, vol. 60, no. 6, pp. 60502-1-60502-15, 2016.11 | |
Metamerism-Based Shading Illusion |
|
 |
This research proposes technology for actualizing artistic illusion that exploits metamerism. Specifically, the purpose of the research relates to automatic calculation of blending ratios of oil paints that cause metamerism to occur under specific light sources. It entails metamerism occurring between four types of object colors under two types of light sources. This enables us to create false shading where the observer recognizes the 2D oil painting as if it is a 3D object with plausible shading. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Takafumi Saneshige, Masashi Baba, Ryo Furukawa, Masahito Aoyama, Shinsaku Hiura, "Metamerism-based Shading Illusion," In The 14th IAPR Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA 2015), pp. 255-258, 2015.05 | |
Mixing Paints for Generating Metamerism Art under 2 Lights and 3 Object Colors |
|
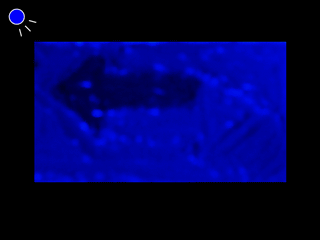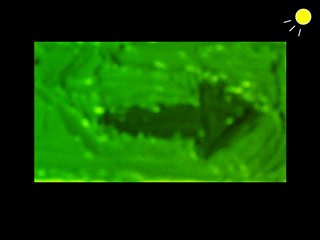 |
This research proposes technology for actualizing artistic illusion that exploits metamerism. Specifically, the purpose of the research relates to automatic calculation of blending ratios of oil paints that cause metamerism to occur under specific light sources. We entails metamerism occurring between three types of object colors under two types of light sources. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Kanami Takahashi, Masashi Baba, Hirooki Aoki, Ryo Furukawa, Masahito Aoyama, Shinsaku Hiura, "Mixing paints for generating metamerism art under 2 lights and 3 object colors," Proc. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (CPCV), pp. 874-882, 2013.12 | |
Polarization-Based Dehazing Using Two Reference Objects |
|
  |
We propose a polarization-based method to enhance the visibility of an image by canceling the haze effect. Our approach is to use two reference objects that are known a priori in estimating the parameters of the haze effect. Once the parameters are known, we can improve the image so that the scene is clearly visible. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Daisuke Akiyama, Masashi Baba, Ryo Furukawa, Shinsaku Hiura, Naoki Asada, "Polarization-based dehazing using two reference objects," Proc. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (CPCV), pp. 852-859, 2013.12 | |
Optimization of 3D Shape Sharpening Filter Based on Geometric Statistical Values |
|
  |
A plaster statue is an object created from a mold made from a stone statue, for example, and into which plaster is poured and hardened. Consequently in this research, by applying a sharpening filter to the 3D shape data of a plaster statue, highlighted contours comparable to those of the original stone statue are reconstructed for the 3D shape data. |
| [1] Masanari Yokomizo, Daisuke Miyazaki, Masashi Baba, Ryo Furukawa, Masahito Aoyama, Shinsaku Hiura, Naoki Asada, "Optimization of 3D Shape Sharpening Filter Based on Geometric Statistical Values," Proc. IAPR Workshop on Machine Vision Applications (MVA2013), pp. 260-263, 2013.5 | |
High Density Shapes Using Photometric Stereo and Laser Range Sensor under Unknown Light-Source Direction |
|
  |
The method proposed in this paper estimates normals to object surfaces by employing the photometric stereo method and combines the estimation with the three-dimensional shape acquired by a laser range sensor. Although the photometric stereo method presumes that light-source directions for each image are known, the proposed method uses its light-source direction estimates. Since the proposed method does not require the light-source directions to be known, it offers the advantage of broad applicability for measurement work. |
| [1] Tomoyuki Kamikawa, Daisuke Miyazaki, Masashi Baba, Ryo Furukawa, Masahito Aoyama, Shinsaku Hiura, Naoki Asada, "High Density Shapes Using Photometric Stereo and Laser Range Sensor under Unknown Light-Source Direction," Proc. IAPR Workshop on Machine Vision Applications (MVA2013), pp. 260-263, 2013.5 | |
A First Introduction to Metamerism Art |
|
  |
Our research project aims to innovate a novel form of artistic illusion by fully making use of metamerism. This paper proposes a method which estimates the mixture ratio of paints that can cause metamerism. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Kazuki Nakamura, Masashi Baba, Ryo Furukawa, Masahito Aoyama, Shinsaku Hiura, Naoki Asada, "A First Introduction to Metamerism Art," SIGGRAPH Asia 2012 Posters, pp. 17:1-17:1, 2012.11-12 | |
Creating Digital Model of Origami Crane through Recognition of Origami States from Image Sequence |
|
  |
In this project, we build a software in order to represent the 3D model of origami crane which has the same message on its surface drawn by the user who folded it in the real world. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Saori Kagimoto, Masashi Baba, Naoki Asada, "Creating digital model of origami crane through recognition of origami states from image sequence," SIGGRAPH ASIA 2010 Posters, pp. 19, 2010.12 | |
Interactive Removal of Shadows from a Single Image Using Hierarchical Graph Cut |
|
  |
We propose a method for extracting a shadow matte from a single image. We use user-supplied hints to solve the problem. The proposed method estimates a fractional shadow matte using a graph cut energy minimization approach. We present a new hierarchical graph cut algorithm that efficiently solves the multi-labeling problems, allowing our approach to run at interactive speeds. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Yasuyuki Matsushita, Katsushi Ikeuchi, "Interactive removal of shadows from a single image using hierarchical graph cut," IPSJ Transactions on Computer Vision and Applications, vol. 2, pp. 235-252, 2010. | |
Photometric Stereo under Unknown Light Sources Using Robust SVD with Missing Data |
|
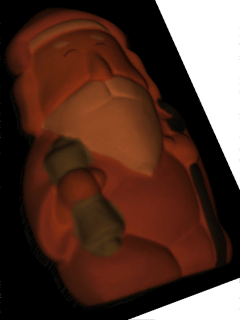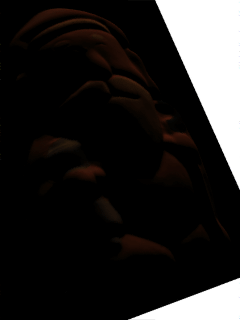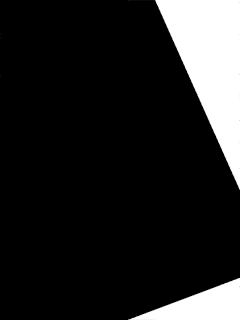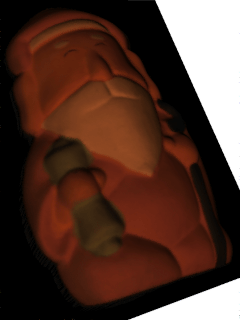  |
Singular value decomposition can solve the photometric stereo problem when the light source direction is unknown; however, it has the critical problem of being sensitive to outliers. We therefore propose a novel singular value decomposition method that is robust to outliers. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Katsushi Ikeuchi, "Photometric stereo under unknown light sources using robust SVD with missing data," Proc. International Conference on Image Processing, 2010.09 | |
Photometric Stereo Using Graph Cut and M-Estimation for a Virtual Tumulus in the Presence of Highlights and Shadows |
|
 |
In this paper, we propose a photometric stereo method that uses a graph cut solution. We formulate the photometric stereo problem to the Markov random field problem, and show how to solve the problem by graph cut. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Katsushi Ikeuchi, "Photometric stereo using graph cut and M-estimation for a virtual tumulus in the presence of highlights and shadows," Proc. Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision in Archaeology, 2010.06 | |
Median Photometric Stereo as Applied to the Segonko Tumulus and Museum Objects |
|
  |
In this paper, we propose a novel photometric stereo method which is robust to the specular reflection of the object surface. We judiciously design the cost function so that the outlier will be automatically removed under the assumption that the object's shape and color are smooth. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Kenji Hara, Katsushi Ikeuchi, "Median Photometric Stereo as Applied to the Segonko Tumulus and Museum Objects," International Journal of Computer Vision, Vol. 86, No. 2-3, pp. 229-242, 2010.01 | |
Wavelet-Texture Method: Appearance Compression by Polarization, Parametric Reflection Model, and Daubechies Wavelet |
|
| First, we separate the images of the object into a diffuse reflection component and a specular reflection component by using linear polarizers. Then, we estimate the parameters of the reflection model for each component. Finally, we compress the difference between the input images and the rendered images by using wavelet transform. At the rendering stage, we first calculate the diffuse and specular reflection images from the reflection parameters, then add the difference decompressed by inverse wavelet transform into the calculated reflection images, and finally obtain the photorealistic image of the object. | |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Takushi Shibata, Katsushi Ikeuchi, "Wavelet-Texture Method: Appearance Compression by Polarization, Parametric Reflection Model, and Daubechies Wavelet," International Journal of Computer Vision, Vol. 86, No. 2-3, pp. 171-191, 2010.01 | |
Estimating Sunlight Polarization Using a Fish-Eye Lens |
|
  |
Unlike previous investigations, we analyze sky polarization patterns when the fish-eye lens is not vertical, since a camera in a general position is effective in analyzing outdoor measurements. We have tilted the measurement system based on a fish-eye lens, a CCD camera, and a linear polarizer, in order to analyze transition of the 180-degree sky polarization patterns while tilting. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Mahdi Ammar, Rei Kawakami, Katsushi Ikeuchi, "Estimating Sunlight Polarization Using a Fish-eye Lens," IPSJ Transactions on Computer Vision and Applications, Vol. 1, pp. 288-300, 2009 | |
Shape Estimation of Transparent Objects by Using Inverse Polarization Raytracing |
|
  |
Polarization raytracing is a combination of conventional raytracing, which calculates the trajectory of light rays, and Mueller calculus, which calculates the polarization state of the light. First, we set an initial value of the shape of the transparent object. Then, by changing the shape, the method minimizes the difference between the input polarization data and the rendered polarization data calculated by polarization raytracing. Finally, after the iterative computation is converged, the shape of the object is obtained. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Katsushi Ikeuchi, "Shape Estimation of Transparent Objects by Using Inverse Polarization Raytracing," IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (PAMI), Vol.29, No.11, pp.2018-2030, 2007.11 | |
3D Digital Archive of the Burghers of Calais |
|
    |
This paper describes our project to fill this need by digitally archiving the bronze statue, The Burghers of Calais. First, we scanned the geometrical shape of the sculpture by using a laser range sensor. After that, we analyzed the resulting three-dimensional data using expert knowledge in the field of art history and technology developed in the fields of computer vision and graphics. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Mawo Kamakura, Tomoaki Higo, Yasuhide Okamoto, Rei Kawakami, Takaaki Shiratori, Akifumi Ikari, Shintaro Ono, Yoshihiro Sato, Mina Oya, Masayuki Tanaka, Katsushi Ikeuchi, Masanori Aoyagi, "3D Digital Archive of the Burghers of Calais," Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Virtual Systems and MultiMedia (VSMM2006)), Vol.4270, pp.399-407, Xi'an, China, 2006.10 | |
Polarization-Based Shape Estimation of Transparent Objects by Using Raytracing and PLZT Camera |
|
    |
In the first part of this paper, we present a method to estimate the shape of transparent objects by using polarization. Our proposed method considers such interreflection by using the raytracing method. Also, we calculate the polarization state of the light using Mueller calculus. The shape of the object is computed by an iterative framework that minimizes the difference between the obtained polarization data and the rendered polarization data. In the second part of this paper, we present an apparatus to measure the polarization state of the light. To analyze the light, we use a material called PLZT whose material state changes with the applied voltage. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Noriyuki Takashima, Akira Yoshida, Eiki Harashima, Katsushi Ikeuchi, "Polarization-based Shape Estimation of Transparent Objects by Using Raytracing and PLZT Camera," in Proceedings of SPIE (Polarization Science and Remote Sensing II, Part of SPIE’s International Symposium on Optics and Photonics 2005), Vol.5888, pp.1-14, San Diego, CA USA, 2005.08 ***Invited talk*** | |
Creating Photorealistic Virtual Model with Polarization Based Vision System |
|
  |
In this paper, we propose the method for creating photorealistic virtual model by using laser range sensor and polarization based image capture system. We capture the range and color images of the object which is rotated on the rotary table. In geometry aspect, an object surface shape is reconstructed by merging multiple range images of the object. In optical aspect, color images are captured under fixed point light source. By using the reconstructed object shape and sequence of color images of the object, parameter of a reflection model are estimated in a robust manner. |
| [1] Takushi Shibata, Toru Takahashi, Daisuke Miyazaki, Yoichi Sato, Katsushi Ikeuchi, "Creating Photorealistic Virtual Model with Polarization Based Vision System," in Proceedings of SPIE (Polarization Science and Remote Sensing II, Part of SPIE’s International Symposium on Optics and Photonics 2005), Vol.5888, pp.25-35, San Diego, CA USA, 2005.08 | |
Transparent Surface Modeling from a Pair of Polarization Images |
|
 |
Unfortunately, the correspondence between the degree of polarization and the surface normal is not one to one. In this paper, we introduce a method to solve the ambiguity by comparing the polarization data in two objects, i.e., normal position and tilted with small angle position. We also discuss the geometrical features of the object surface and propose a method for matching two sets of polarization data at identical points on the object surface. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Masataka Kagesawa, Katsushi Ikeuchi, "Transparent Surface Modeling from a Pair of Polarization Images," IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (PAMI), Vol.26, No.1, pp.73-82, 2004.01 | |
Polarization-based Inverse Rendering from a Single View |
|
  |
This paper presents a method to estimate geometrical, photometrical, and environmental information of a single-viewed object in one integrated framework under fixed viewing position and fixed illumination direction. The proposed method estimates the 3D shape by computing the surface normal from polarization data, calculates the texture of the object from the diffuse only reflection component, determines the illumination directions from the position of the brightest intensity in the specular reflection component, and finally computes the surface roughness of the object by using the estimated illumination distribution. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Robby T. Tan, Kenji Hara, Katsushi Ikeuchi, "Polarization-based Inverse Rendering from a Single View," in Proceedings of International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV2003), pp.982-987, Nice, France, 2003.10 | |
Determining Surface Orientations of Transparent Objects Based on Polarization Degrees in Visible and Infrared Wavelengths |
|
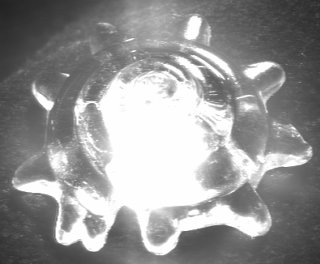  |
We present a new method for obtaining surface orientations of transparent surfaces through analysis of the degree of polarization in surface reflection and emission in visible and far-infrared wavelengths, respectively. This parameter, the polarization degree of reflected light in the visible wavelengths, is used for determining the surface orientation at a surface point. The polarization degree at visible wavelengths provides two possible solutions, and the proposed method uses the polarization degree at far-infrared wavelengths to resolve this ambiguity. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Megumi Saito, Yoichi Sato, Katsushi Ikeuchi, "Determining surface orientations of transparent objects based on polarization degrees in visible and infrared wavelengths," Journal of Optical Society of America A (JOSA A), Vol. 19, No. 4, pp.687-694, 2002.04 | |
The Great Buddha Project: Modelling Cultural Heritage through Observation |
|
    |
For geometric model creation, we have developed a two-step method: simultaneous alignment and volumetric view merging. For photometric model creation, we have developed the eigen-texture rendering methods, which automatically create photorealistic models by observing the real objects. For the integration of virtual objects with real scenes, we have developed a method that renders virtual objects based on real illumination distribution. We have applied these component techniques to constructing a multimedia model of the Great Buddha of Kamakura, and demonstrated their effectiveness. |
| [1] Daisuke Miyazaki, Takeshi Ooishi, Taku Nishikawa, Ryusuke Sagawa, Ko Nishino, Takashi Tomomatsu, Yutaka Takase, Katsushi Ikeuchi, "The Great Buddha Project: Modelling Cultural Heritage through Observation," in Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Virtual Systems and MultiMedia (VSMM2000), pp.138-145, Gifu, Japan, 2000.10 ***Best overall paper*** | |